by M4t_6_onL | May 9, 2022 | Functions, Geometry
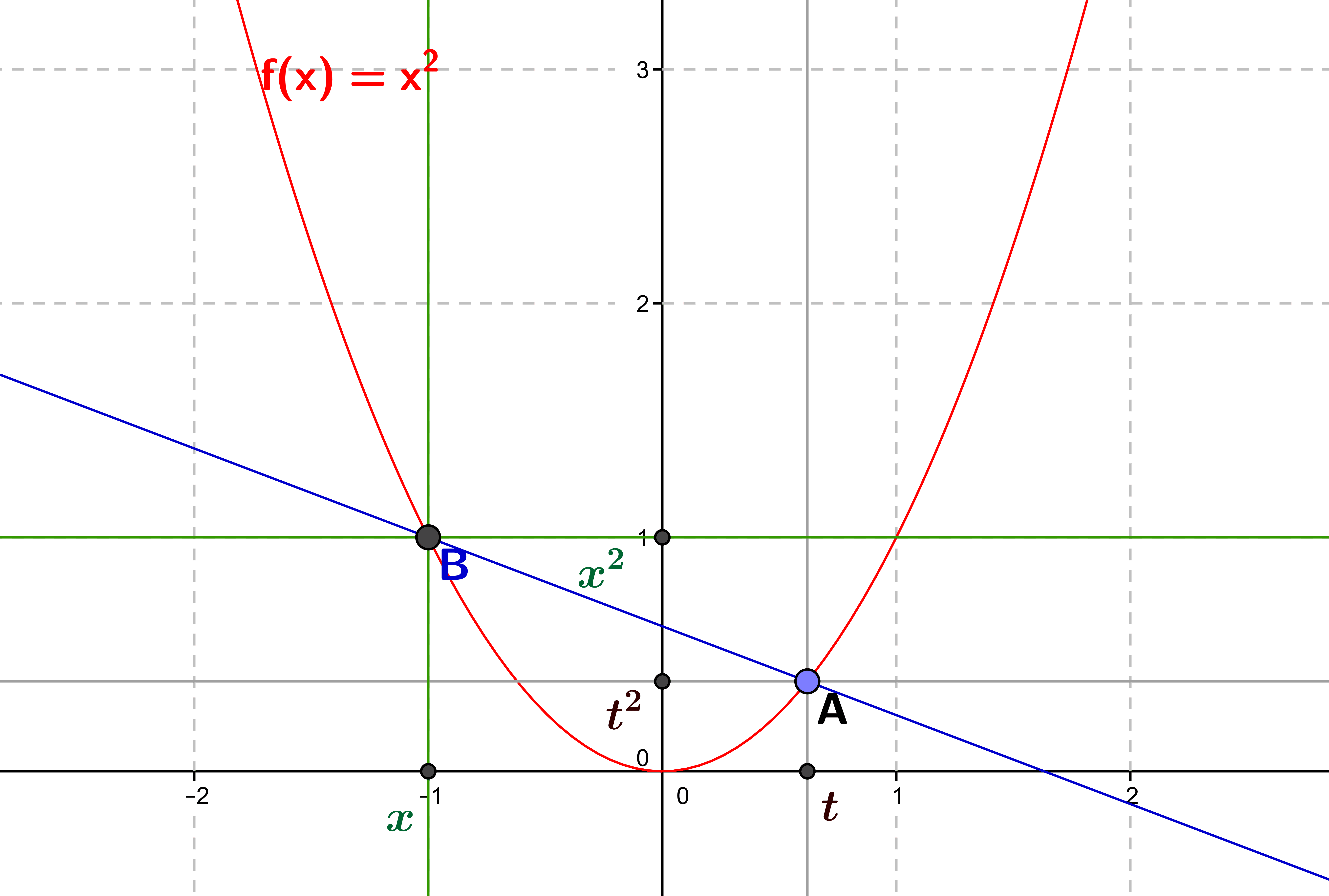
The derivative of a function is its instantaneous variation, i.e. the slope of the tangent to the graphical representation of the function at that point. 1. General idea: an instantaneous variation We place ourselves here in the framework of functions of a real...
by M4t_6_onL | Apr 28, 2022 | Algebra, Geometry
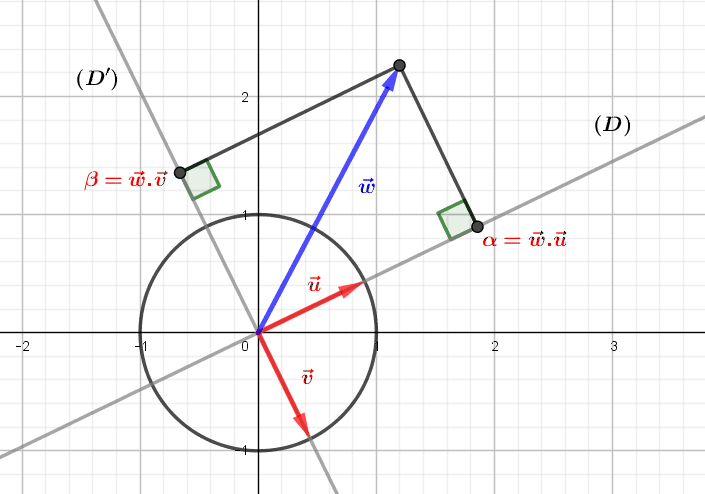
The linear transformations of the Euclidean plane are the invertible linear applications, i.e. of non-zero determinant. They allow us to move from one basis of the plane to another, and the orthogonal transformations, i.e. the vectorial isometries, exchange the...
by M4t_6_onL | Apr 23, 2022 | Algebra, Geometry
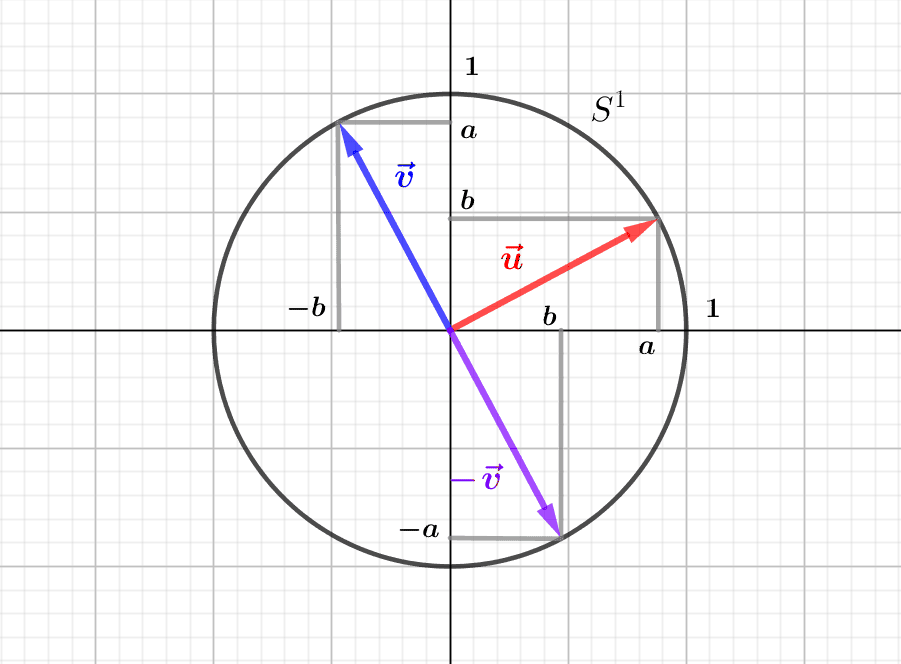
The representation of the Euclidean plane as the Cartesian product \(\mathbb R^2\) allows us to decompose any vector of the plane into two coordinates, its abscissa and its ordinate. This decomposition is linked to a particular and natural “representation...
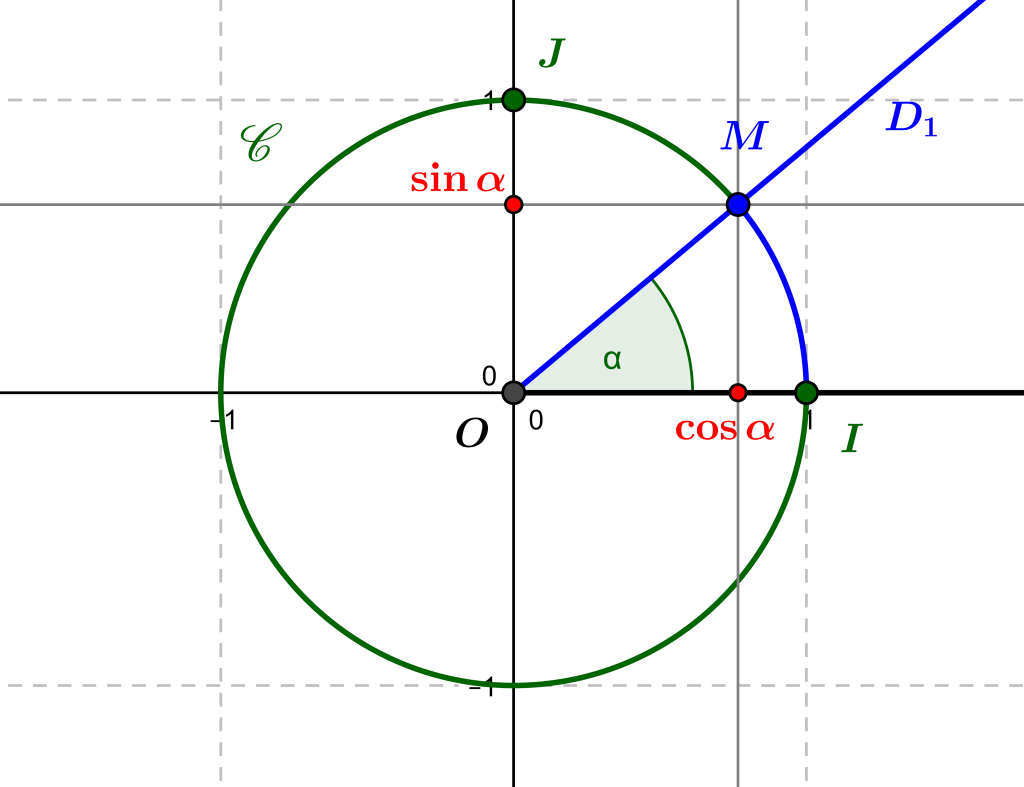
by M4t_6_onL | Mar 14, 2022 | Trigonometry
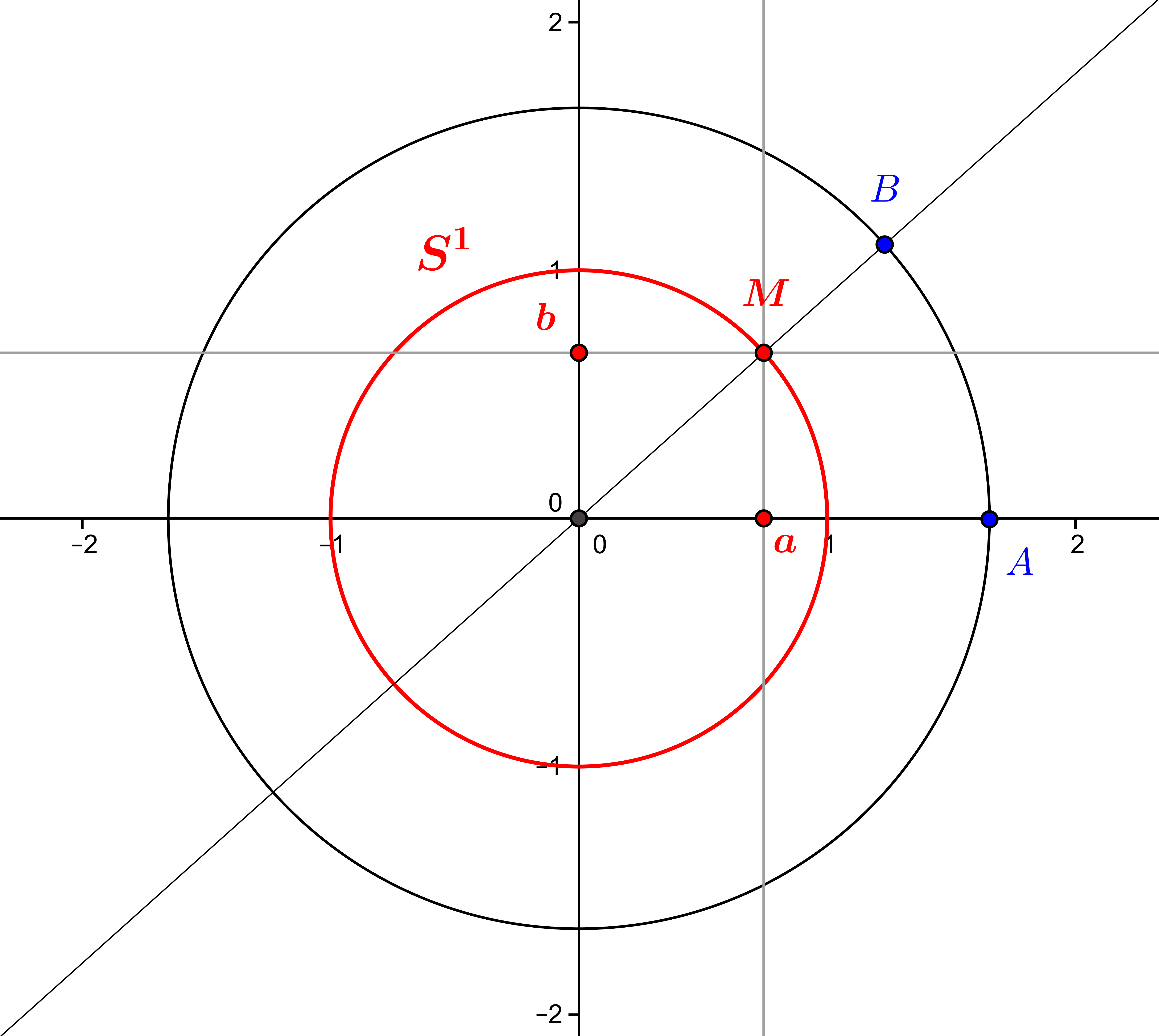
The trigonometric circle allows us to define the cosine, sine and tangent of an oriented angle, and to give an interpretation through Thales’ and Pythagoras’ theorems. Introduction: trigonometry and functions Trigonometry is the study of the relationships...