by M4t_6_onL | Dec 8, 2022 | Algebra, Geometry
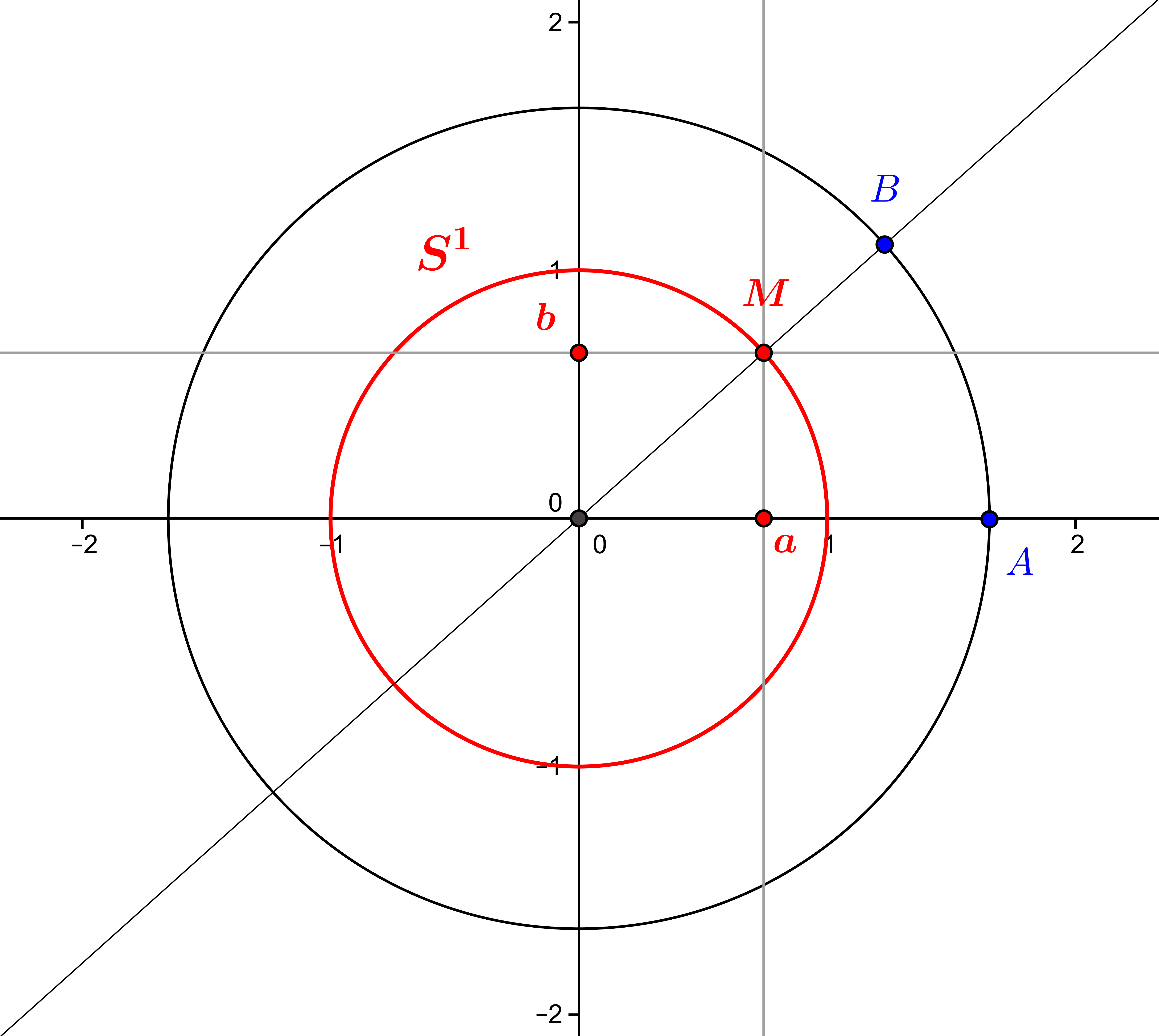
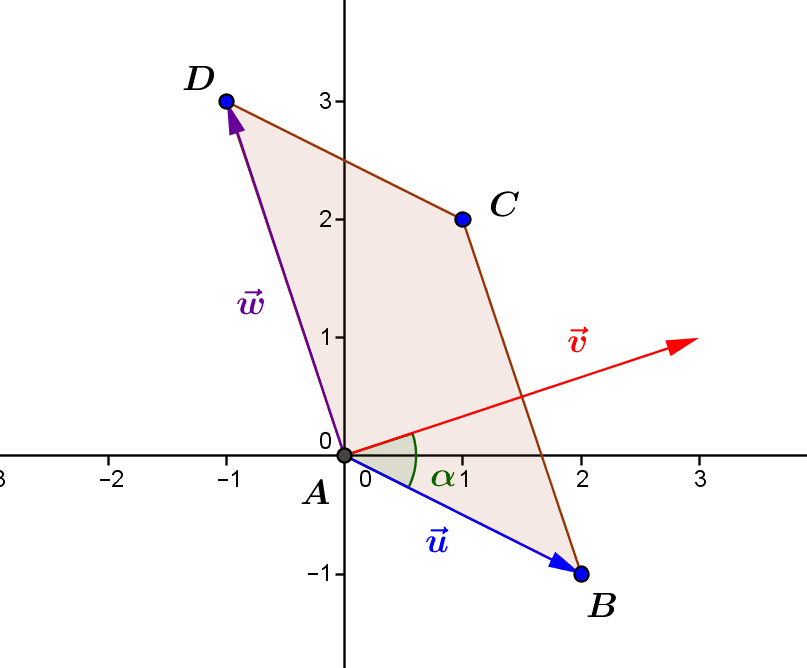
The scalar or dot product of two vectors in real space is a real number that takes into account the direction, sense and magnitude of both vectors. 1.The natural scalar product in the Euclidean plane 1.1.From the distance between two points to the scalar product In...
by M4t_6_onL | May 9, 2022 | Functions, Geometry
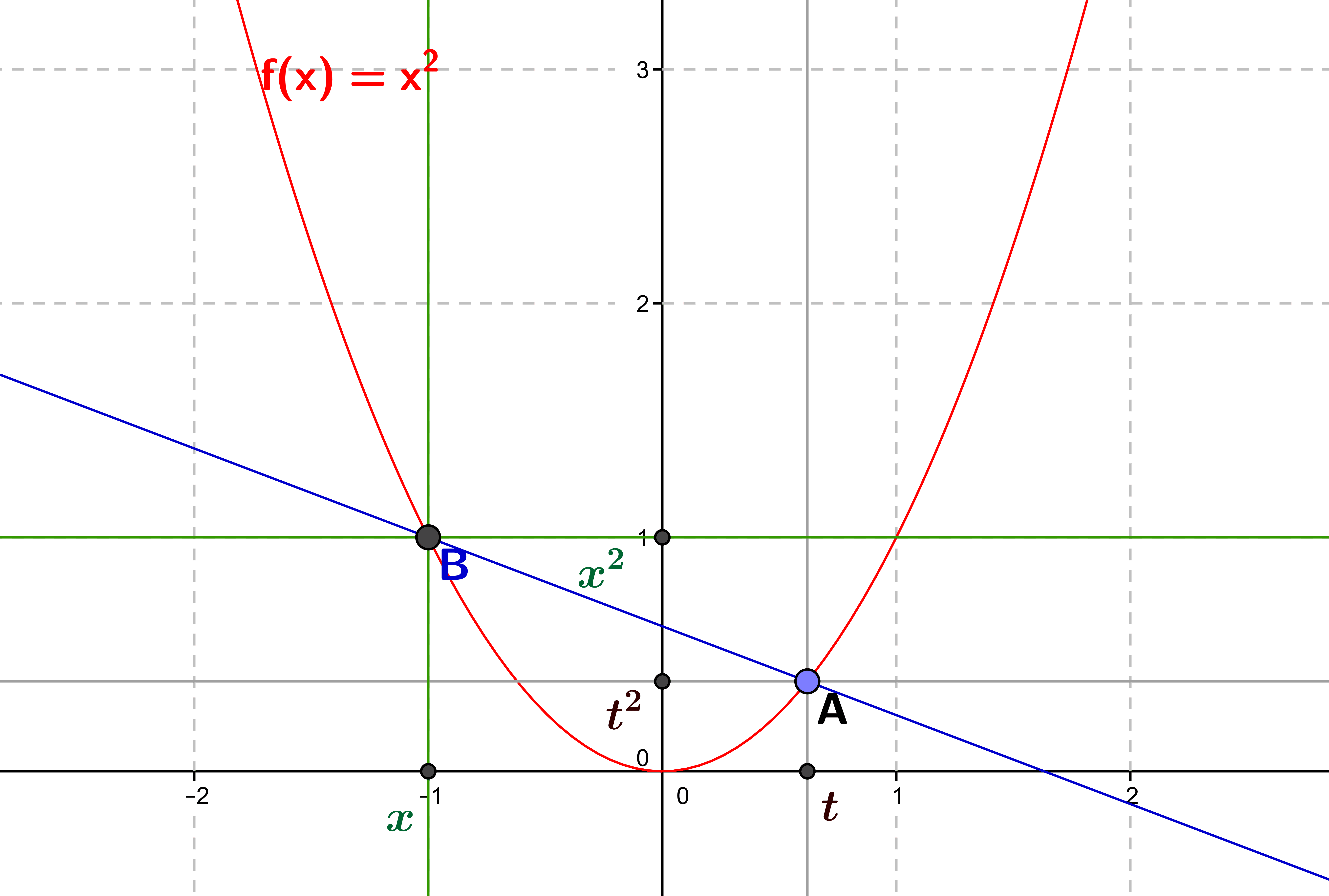
The derivative of a function is its instantaneous variation, i.e. the slope of the tangent to the graphical representation of the function at that point. 1. General idea: an instantaneous variation We place ourselves here in the framework of functions of a real...
by M4t_6_onL | Apr 28, 2022 | Algebra, Geometry
The linear transformations of the Euclidean plane are the invertible linear applications, i.e. of non-zero determinant. They allow us to move from one basis of the plane to another, and the orthogonal transformations, i.e. the vectorial isometries, exchange the...
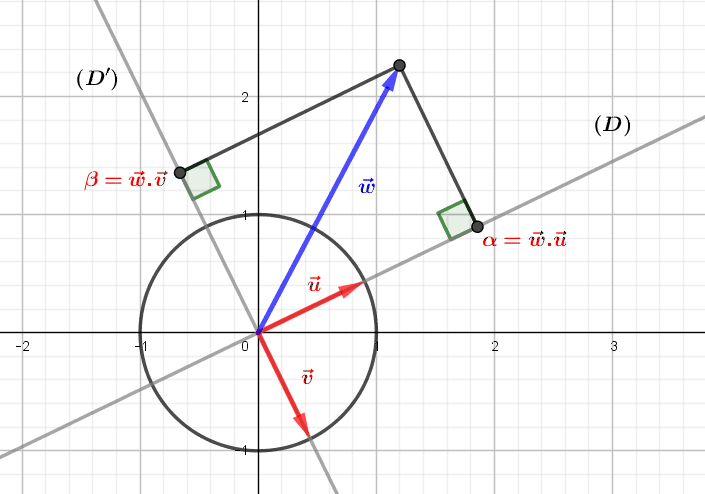
by M4t_6_onL | Apr 23, 2022 | Algebra, Geometry
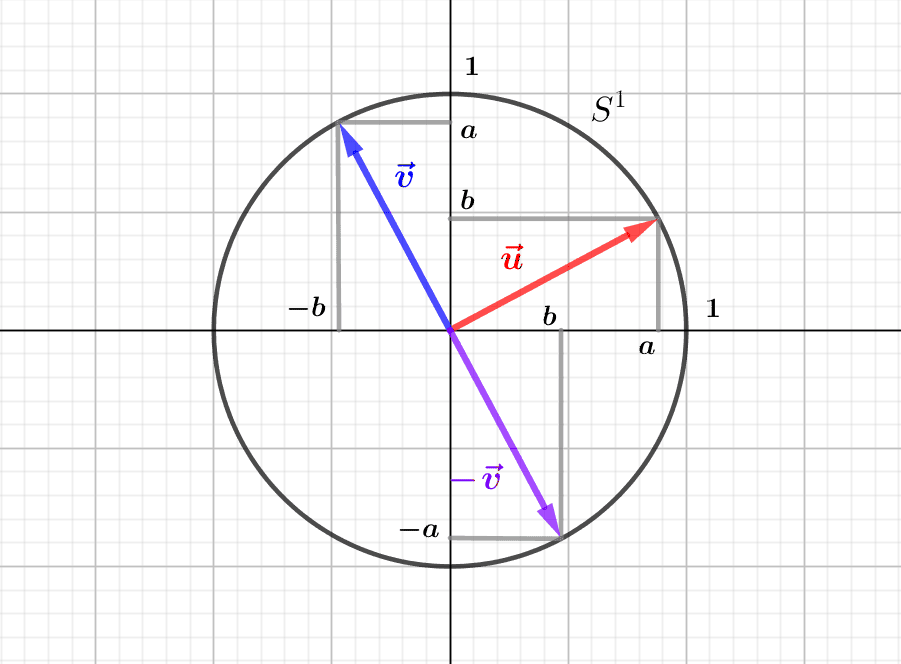
The representation of the Euclidean plane as the Cartesian product \(\mathbb R^2\) allows us to decompose any vector of the plane into two coordinates, its abscissa and its ordinate. This decomposition is linked to a particular and natural “representation...
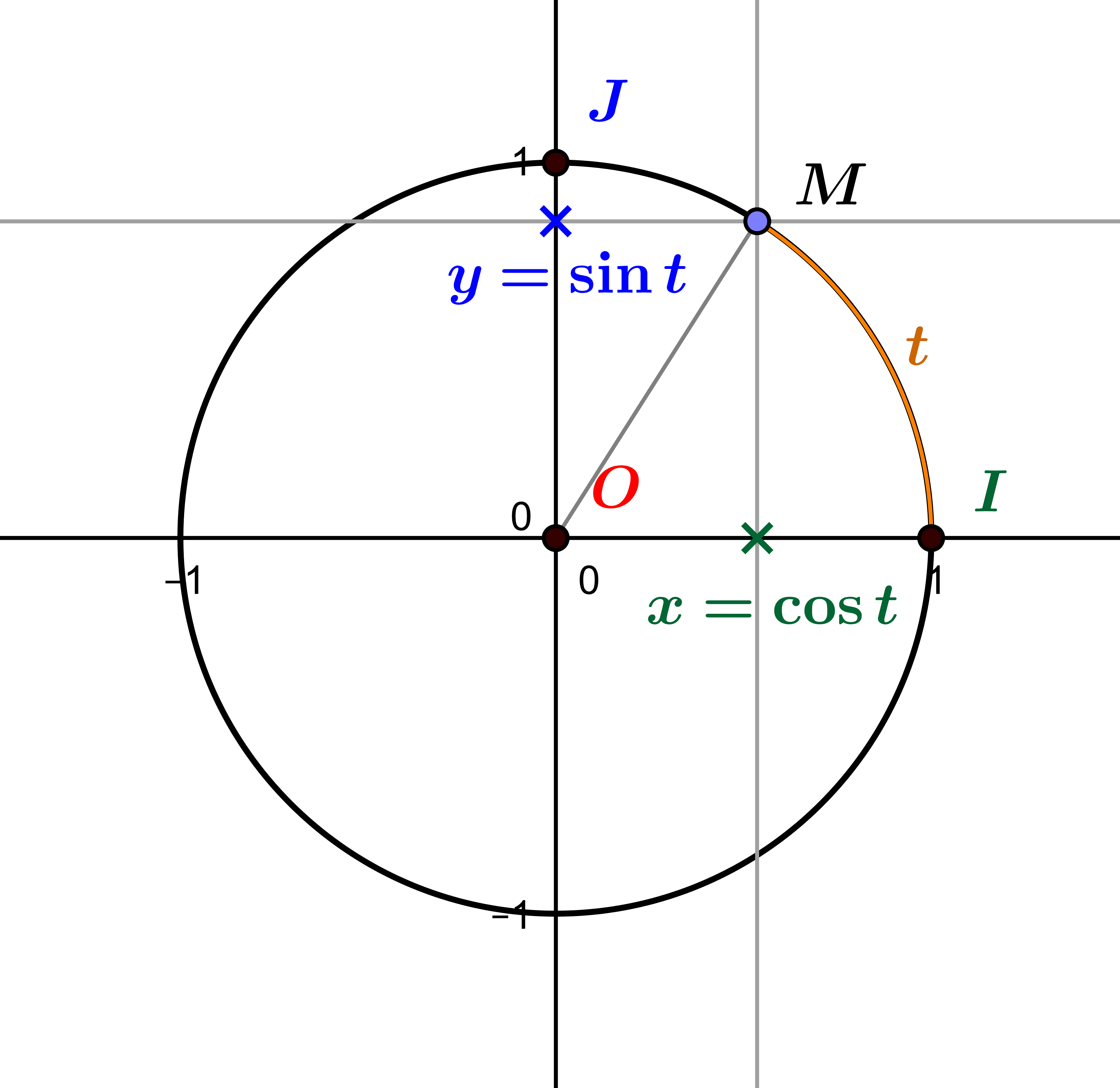
by M4t_6_onL | Jan 28, 2022 | Functions, Geometry
The definition of a circle is simple: it is a set of points located at the same distance from a given point. This distance is called the radius and this point is called the centre of the circle. The circle with centre \((-1,-3/2)\) and radius \(\sqrt 6\) 1. Circles as...